Lecture 19: Regression.Model Building
Exam 4
Exam 4 will be Saturday, Dec 3 from 5:30pm-7:30pm
Everyone MUST take the exam at this time
If you have a serious conflict, see me in person—do not send an email– at
least one week ahead of the exam date with documentation of your
conflict and I MAY allow you to take the exam early (NOT late).
Examples of valid reasons for rescheduling your exam: you have surgery scheduled for that date, it’s your sister’s wedding date
Examples of non-valid reasons that will not be approved: you forgot to ask off at work and were put on the schedule; you always drive
your Grandma to bingo on Saturday nights
If you don’t take the exam at the scheduled time or receive approval to
take the exam early, this will have to be your drop
You do not have to take Exam 4 if you’re happy with your grade as it is now
Model Building
Ideas Already Discussed
QN Independent Variables
QL Independent Variables
Quadratic Terms
Interaction Terms
Model Building
Begin with a complete 2nd-order model and
build down to the most useful (parsimonious)
model.
Three steps to building the complete 2nd-order
model:
1. Add in all QN (linear and quadratic) terms to the
model
2. Add in all QL (only) terms to the model
3. Interact all the terms from steps 1 and 2
nd
Complete 2 -order Model
Example: Homework Data – one QN and one QL
with two levels.
x1 – QN, x2 – QL(2)
1 𝑖𝑓 𝐶𝑎𝑚𝑎𝑟𝑜
𝑋2 = ቊ
0 𝑖𝑓 𝑀𝑢𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑔
Model: E(y) = 0 + 1×1 + 2×12 + 3×2 + 4x1x2+ 5×12 x2
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
nd
Complete 2 -order Model
Example: One QN and one QL with three levels
(ex., Camaro, Mustang, Charger).
1 𝑖𝑓 𝐶𝑎𝑚𝑎𝑟𝑜
𝑋2 = ቊ
0
𝑖𝑓 𝑛𝑜𝑡
x1 – QN, x2, x3 – QL(3)
𝑋3 = ቊ
Model: E(y) = 0 + 1×1 + 2×12 + 3×2 + 4×3
Step 1
Step 2
+ 5x1x2+ 6×12 x2 + 7x1x3+ 8×12 x3
Step 3
1 𝑖𝑓 𝑀𝑢𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑔
0
𝑖𝑓 𝑛𝑜𝑡
Testing the Model
Global-F Test – Tests the entire model at one time.
Model: E(y) = 0 + 1×1 + 2×12 + 3×2 + 4x1x2+ 5×12 x2
Test: Ho: 1 = 2 = 3 = 4 = 5 = 0
Ha: At least one 0
Test Statistic/P-value: (From Printout)
Conclusion: Reject Ho. Something works in the model.
Fail to Reject Ho. Stop!
(Not on HW 3. Only time α can exceed .10)
Testing the Model
Partial-F Test – Tests a portion of the model.
Full Model: E(y) = 0 + 1×1 + 2×12 + 3×2 + 4x1x2+ 5×12 x2
Reduced Model: E(y) = 0 + 1×1 + 3×2 + 4x1x2
Example: test the quadratic component in the model.
Test: Ho: 2 = 5 = 0
Ha: At least one 0
Test Statistic/P-value: (From Printout)
Conclusion: Reject Ho. The quadratic terms work. Keep them.
FTR Ho. Drop the quadratic terms.
Testing the Model
The Partial-F test compares two models (the one that has the tested
terms in it to the one that drops them out) to determine which model
is better at predicting y.
STATISTIX program refers to the Partial-F test as the Best Subset
Regressions Test
The model terms are separated into two classifications:
•Non-Forced: the terms we wish to test
•Forced: the terms that appear in both models
Testing the Model
T-Test – Tests a single term in the model.
Model: E(y) = 0 + 1×1 + 3×2 + 4x1x2
Reduced Model: E(y) = 0 + 1×1 + 3×2
Example: test the interaction component in the model.
Test: Ho: 4 = 0
Ha: 4 ≠ 0
Test Statistic/P-value: (From Printout – may need to adjust)
Conclusion: Reject Ho. The interaction terms work. Keep it.
FTR Ho. Drop the interaction term.
Model Testing in Statistix
Global F-Test
•Statistics → Linear Models → Linear Regression
•Fit the full model and use F-test p-value
Partial F-Test
•Statistics → Linear Models → Best Subsets Regressions
•Terms to be tested – Non-forced variables
•Terms in reduced model – Forced variables
T-Test
•Statistics → Linear Models → Linear Regression
•Fit the full model and use appropriate t-test p-value
Model Building – Game Plan
Global F-Test
FTR Ho
Model 1
Reject Ho
Quadratics Test
Model 1 vs. 2
Reject Ho
Interactions
FTR Ho
Model 1 vs. 3
FTR Ho
Reject Ho
QL Test (if needed)
1
3
FTR Ho
Reject Ho
Model 3 vs. 5
Reject Ho
QN Test (if needed)
Model 2 vs. 4
2
Model 4 vs. 6
Reject Ho
FTR Ho
FTR Ho
Model 4 vs. 7
5
Reject Ho
4
6
FTR Ho
7
Practice Questions
When building your model, in what order do you add the QL variables, the
QN variables, the quadratics, and the interactions?
• QN linear and QN quadratics
• QL
• Interactions amongst the above
When will you have interactions with QL variables?
• When there is more than one QL variable
Practice Questions
For HW3, what is an acceptable alpha for your global F test?
• As high as it needs to be to reject the null hypothesis!
In real life, what do you we if the p-value for the global F test is .05 or higher?
• STOP! Nothing in this model works; no further testing
Miko
MIKO
Boomer
Mako
Essay Writing Service Features
Our Experience
No matter how complex your assignment is, we can find the right professional for your specific task. Achiever Papers is an essay writing company that hires only the smartest minds to help you with your projects. Our expertise allows us to provide students with high-quality academic writing, editing & proofreading services.
Free Features
Free revision policy
$10Free bibliography & reference
$8Free title page
$8Free formatting
$8How Our Dissertation Writing Service Works
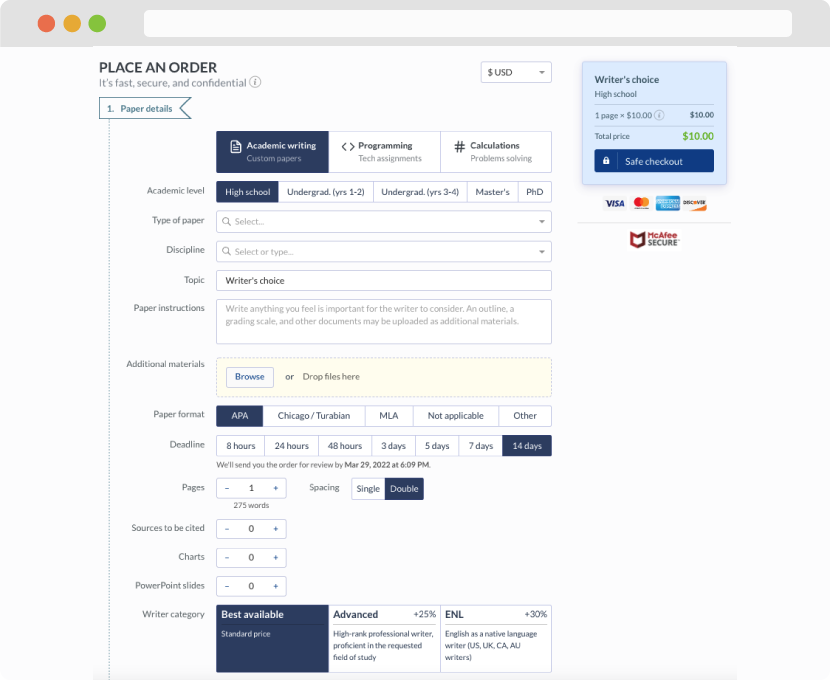
First, you will need to complete an order form. It's not difficult but, if anything is unclear, you may always chat with us so that we can guide you through it. On the order form, you will need to include some basic information concerning your order: subject, topic, number of pages, etc. We also encourage our clients to upload any relevant information or sources that will help.
Complete the order form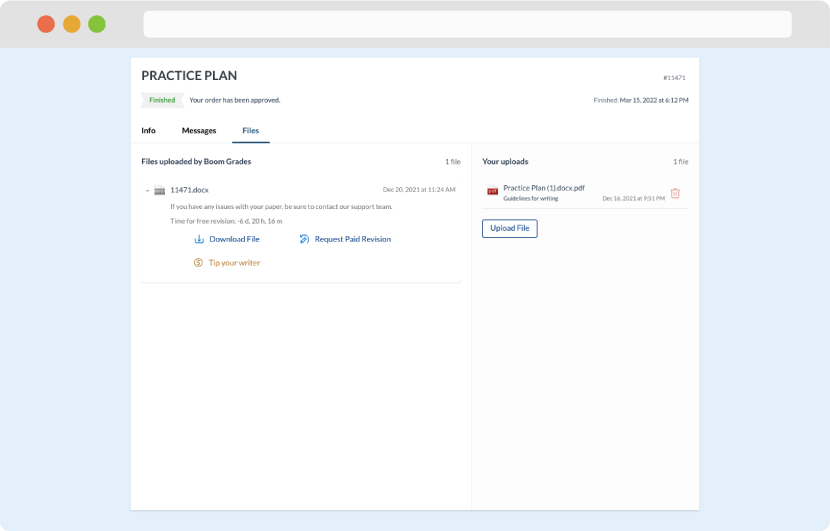
Once we have all the information and instructions that we need, we select the most suitable writer for your assignment. While everything seems to be clear, the writer, who has complete knowledge of the subject, may need clarification from you. It is at that point that you would receive a call or email from us.
Writer’s assignment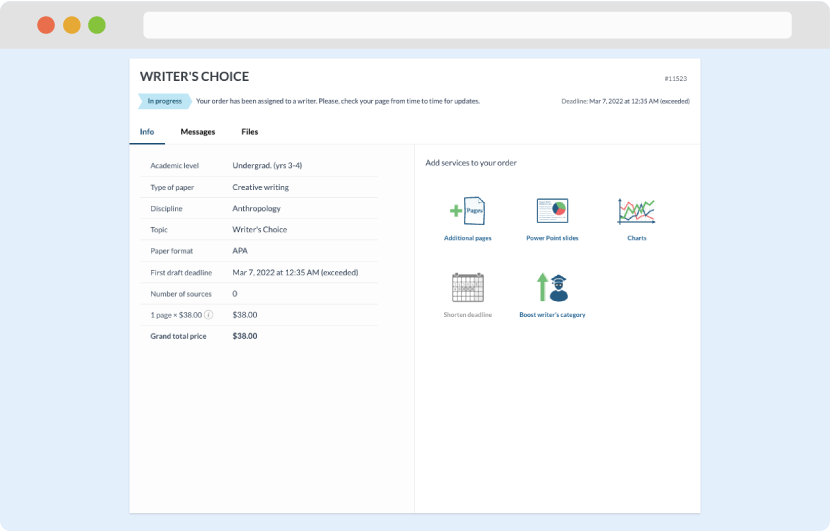
As soon as the writer has finished, it will be delivered both to the website and to your email address so that you will not miss it. If your deadline is close at hand, we will place a call to you to make sure that you receive the paper on time.
Completing the order and download